This series has been funded in part by the Pennsylvania News Media Association.
This item is available in full to subscribers.
We have recently launched a new and improved website. To continue reading, you will need to either log into your subscriber account, or purchase a new subscription.
If you are a digital subscriber with an active subscription, then you already have an account here. Just reset your password if you've not yet logged in to your account on this new site.
If you are a current print subscriber, you can set up a free website account by clicking here.
Otherwise, click here to view your options for subscribing.
Please log in to continue |

As the Riverkeeper for the Lower Potomac River, Dean Naujoks is one of the leading advocates for cleaning up that 405-mile waterway, which originates in West Virginia before snaking through Washington, D.C., and emptying into the Chesapeake Bay.
Naujoks believes in the ability of green infrastructure to help clean up the historically polluted Potomac and he said there’s “no bigger fan” of the concept.
But only to a point.
Naujoks said that about a decade ago, when the DC Water & Sewer Authority was renegotiating its agreement with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency over its combined sewer overflows, the authority pressed for a green-centric plan similar to Philadelphia’s, which had been approved and even championed by the EPA just a few years earlier.
But with the Potomac and its tributaries heavily choked by sewage and other pollution, Naujoks was skeptical.
“There was actually an environmental film festival, where there was a short film on rain barrels and green infrastructure,” Naujoks recalled. “Everybody’s clapping and applauding, and I had to get up at the end and say, ‘Hey, I want to know what you’re doing to meet water quality standards?’”
“We were the ones that kind of came and killed the party,” he added.
Green infrastructure needs the right setting
Naujoks, echoing some critics of the Philadelphia Water Department’s Green City, Clean Waters, program said he simply was not convinced that spending billions of dollars on large-scale green infrastructure was going to adequately clean up the Potomac and a primary tributary, the Anacostia River, to meet regulatory requirements.
In his experience, the most successful green infrastructure projects were those newly built in large, open-space settings. Planners run into trouble when they try to retrofit them into dense urban areas like those around the Beltway.
“The amount of stormwater that can be picked up from these kinds of pocket parks and retrofits is” inadequate, Naujoks said. Still, Naujoks said he believes all new development should be required to have green infrastructure.
Nancy Stoner, the president of his organization who previously served as assistant administrator in the EPA’s Office of Water, agrees.
“In addition to working in open space areas such as new developments, green infrastructure can also work in redevelopment/retrofit situations,” Stoner wrote in an email. “But it has to be implemented aggressively – not just a rain garden or green roof here or there but everywhere – and that can be expensive.”
Tunnels as an alternative
Naujoks said his group threw its support behind an approach that still invested heavily in traditional infrastructure, like tunnels.
In the end, that philosophy largely won the day. In 2016, DC Water finalized a $3.3 billion plan called the Clean Rivers Project. John Lisle, a spokesman for DC Water, said that only about $98 million of that sum is directed toward green infrastructure.
Moreover, the authority’s plan primarily uses green infrastructure to clean a tributary called Rock Creek, where DC Water had the most confidence it would serve as a suitable substitute for traditional methods.
“This approach is feasible in this sewershed because of its low overflow volumes and because of the lower density of development in the sewershed,” the authority concluded.
DC Water then plowed most of its funding into the construction of six underground sewage storage tunnels scattered throughout its coverage area. When fully complete, they will stretch a combined 18 miles and store 249 million gallons of sewage during rain events.
Workers began drilling a four-tunnel system along the Anacostia in 2011 and completed it in 2023, a year ahead of schedule and on budget, Lisle said.
The authority calculates the system now captures about 98 percent of sewage overflows, and the Riverkeepers there are pushing for the first legal swimming event in the Anacostia in more than 50 years.
“The Anacostia is definitely improving,” Naujoks said. “In general, we have a lot more swimmable days than we used to.”
Green with envy
A safe swim in the Schuylkill River is precisely Nick Pagon's dream. A former Philadelphia School District teacher, Pagon became a clean water advocate after starting a boat-building nonprofit for city kids.
He fears the city’s Green City, Clean Waters plan isn’t on track to deliver water improvements comparable to the ones around the nation’s capital.
Even more concerning for Pagon is his belief that PWD isn’t interested in fundamentally re-evaluating its approach until its present agreement with the EPA expires in 2036.
“It seems it’s, ‘Let’s wait until 2036 and see where we stand,’” Pagon said. “But we already know what the probable outcome will be, which is they haven’t achieved the water quality objectives, and they have to start again.”
The choice for Germantown
Underneath the Northwest Philadelphia neighborhood of Germantown lies the city’s most polluting combined sewer line, which runs west to east across North Philadelphia and dumps hundreds of millions of gallons of diluted sewage into the Frankford Creek each year.
But the undersized pipe also can’t drain Germantown and surrounding neighborhoods quickly enough during major storms, exacerbating chronic flooding, leading to basement sewage backups and causing up to $8.72 million in property damages each year, the PWD’s own estimates show.
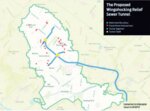
Germantown is also the site of the only D.C.-esque tunnel proposal the Philadelphia Water Department currently has on the books.
Early assessments estimate that placing a large tunnel there could reduce flood depths in Germantown by as much as 80 percent and eliminate up to two-thirds of basement backups.
In 2019, contractor CH2M HILL Engineers delivered a 17-page study to PWD identifying potential traditional infrastructure projects to help in Germantown, such as a large tunnel.
The next year, PWD convened a community task force to discuss flooding in the area.
Employees said a decision was made to further study the possibility of a tunnel and the PWD opened a new contract for a preliminary assessment. While the department has selected an engineering firm for the work, it is still seeking federal funding to pay for it.
The proposal is now more than a year behind schedule and has no apparent start date on the horizon, while the $5 million price tag for the study represents only a tiny fraction of what the PWD is spending on Green City, Clean Waters.
PWD disputed the notion that the new study is superfluous, saying it is “necessary to confirm additional areas of feasibility and optimize our design.”
“PWD is very diligent at utilizing its funding and does not intentionally delay projects,” it added.
Tunnel not as costly as once thought
Internal PWD documents show that costs to construct such a storage tunnel are likely substantially lower than original estimates predicted in 2009, when the push for a green infrastructure-first approach was underway.
In 2022, the PWD working group established to re-evaluate costs held a meeting on tunneling options.
The information presented showed that in 2009, PWD estimated that a large sewer tunnel, depending on its width and length, could cost between about $400 million and $1.7 billion.
But more recent cost estimates for a tunnel under Germantown came in significantly lower after examining real-world projects like the D.C. tunnels.
New estimates relying on real-world data show that a 20-foot-diameter tunnel stretching more than five miles could be built for about $750 million, compared to a 2009 estimate that ran over $1 billion.
“Over time, there is the benefit of data,” the PWD said. “Current estimates utilize additional national bid data points compared to conceptual cost data used in 2009.”
Josh Lippert, a professional floodplain manager and former chairman of Philadelphia’s Flood Risk Management Task Force, believes the reluctance to proceed with a Germantown tunnel is largely due to a lack of political pressure.
Lippert noted that in trendy Northern Liberties, PWD is spending more than $93.5 million on traditional infrastructure to fix a buried Cohocksink Creek combined sewer line and curb flooding. But in Germantown, a predominantly Black and working class neighborhood where a 27-year-old mother of one drowned while driving in 2011, the status quo remains.
“We’ll continue to have fatalities because they did a million-dollar study that has now sat on the shelf because there is no political action to take that forward,” Lippert said.
The PWD also disputed this idea, noting the Germantown project is about five times the scale of Northern Liberties.
It said the costs of the Germantown flood relief project “will dwarf expenditures in the Cohocksink flood relief project,” adding, “It would be inappropriate to draw a comparison of expenditures at two very different points in the process.”
This series has been funded in part by the Pennsylvania News Media Association Foundation.